Semester: BE Computer Sem-5
Question: Block diagram of 8085 microprocessor
Answer :
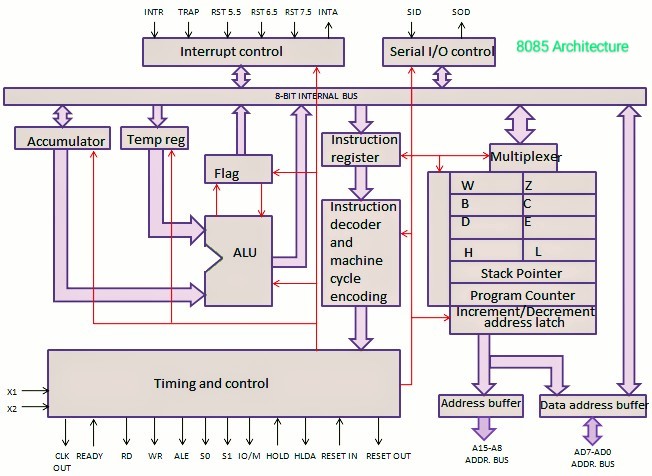
Fig. block diagram of 8085 micro processor
ALU: Arithmetic and logical unit perform the computing functions. That includes the accumulator, temporary reg. ALU ckt. & five flags.
The temporary reg. is used to hold data during an ALU operation. The results is stored in accumulator & flags are set or reset according to the results of the operations.
Flags:
S-sign flag: After execution of an arithmetic or logical operation, if bit D7 of the result is 1 the sign flag is set.
D7 is reserved for indicating the sign & remaining 7-bit are used to represent the magnitude of a no.
AC-Auxiliary Carry Flag: In an arithmetic operation when a carry is generated by digit D3 & passed on to digit D4 the AC flag is set. Only used for BCD. Not for jump instruction.
Z-Zero flag: The Zero flag is set if the ALU operation results is 0 & the flag is reset if the result is not 0.
P-Parity Flag: After arithmetic operations if the results has an even no. of 1’s the flag is set if odd no. of 1’s the flag is reset.
For ex. 0000 0011 – P flag set.
CY-Carry Flag: If an arithmetic operations result in a carry the carry flag is set otherwise reset.
The bit position reserved for flag in flag reg:
Timing & Control unit: This unit synchronizes all the microprocessor operations with the clock & generates the control signals necessary for communication between the microprocessor & peripherals.
Instruction register & Decoder: The instruction register & decoder are part of ALU. When an instruction is fetched from memory it is loaded in the instruction register. The decoder decodes the instruction & establishes the sequence of event to follow IR is not programmable & cannot be accessed through any instruction.
Register Array: Two additional register called temporary register W & Z. are included in register array these register are used to hold 8-bit data during the execution of some instructions.